What is Radon?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas.
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can cause lung cancer. Radon gas is inert, colorless and odorless. Radon is naturally in the atmosphere in trace amounts. In the great outdoors, radon disperses rapidly so generally, it is not a health issue. Health issues from radon exposure are mostly produced indoors. Breathing radon over time increases your risk of lung cancer. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. Nationally, the EPA estimates that about 21,000 people die each year from radon-related lung cancer. Only smoking causes more lung cancer deaths.
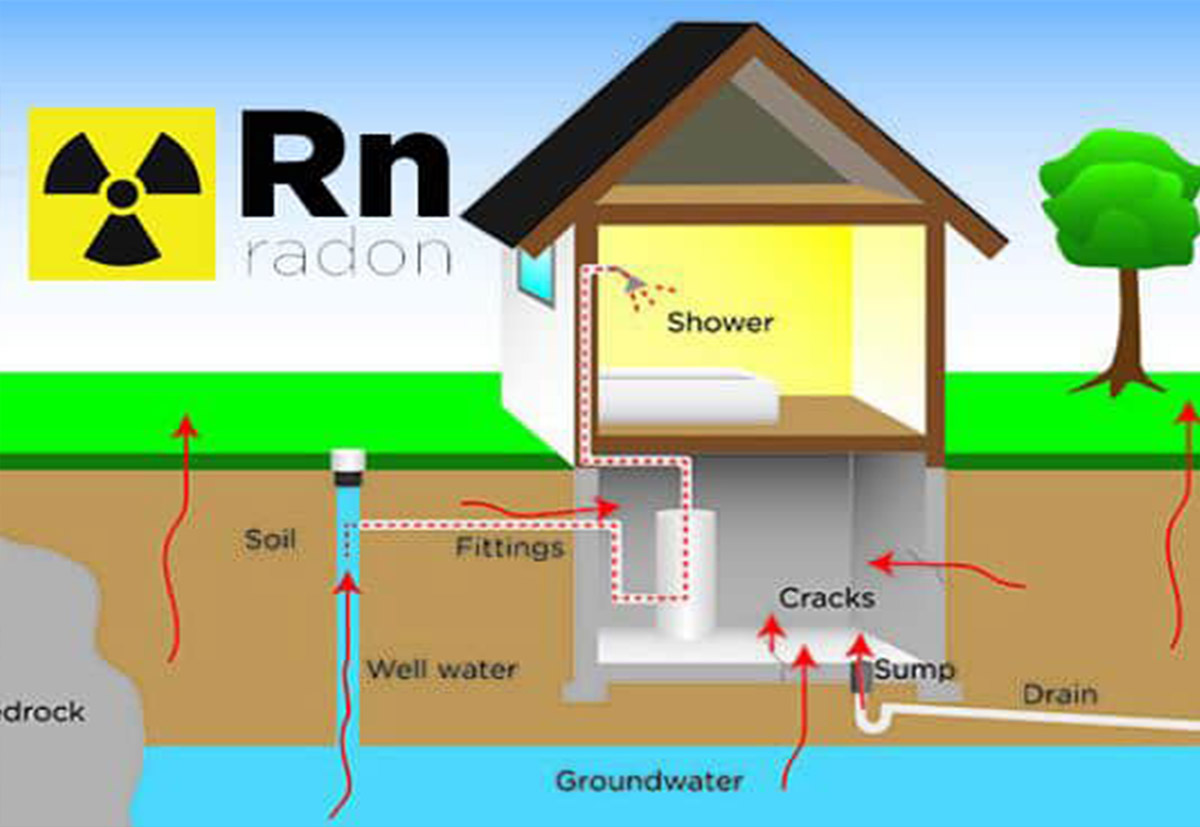
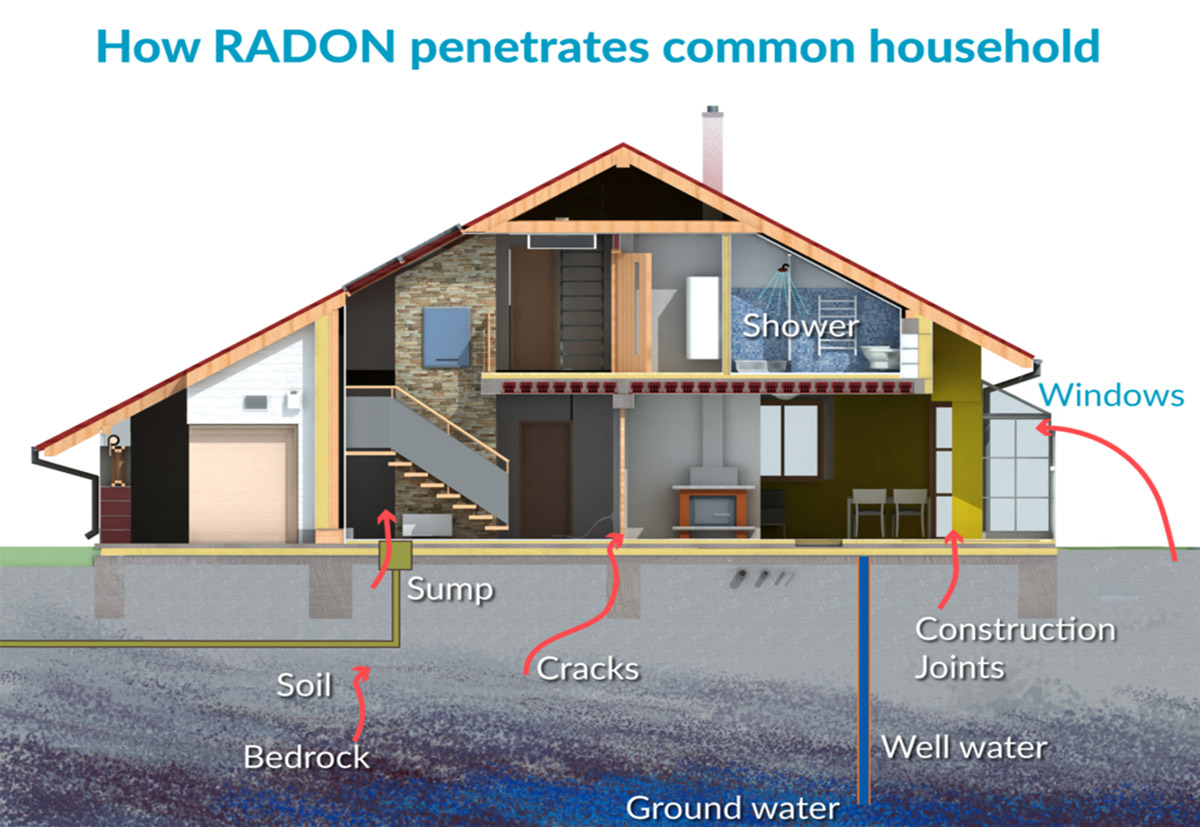
Most harmful radon exposure occurs inside homes, schools and workplaces.
Radon gas becomes trapped indoors after it enters buildings through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Indoor radon can be controlled and managed with proven, cost-effective techniques.
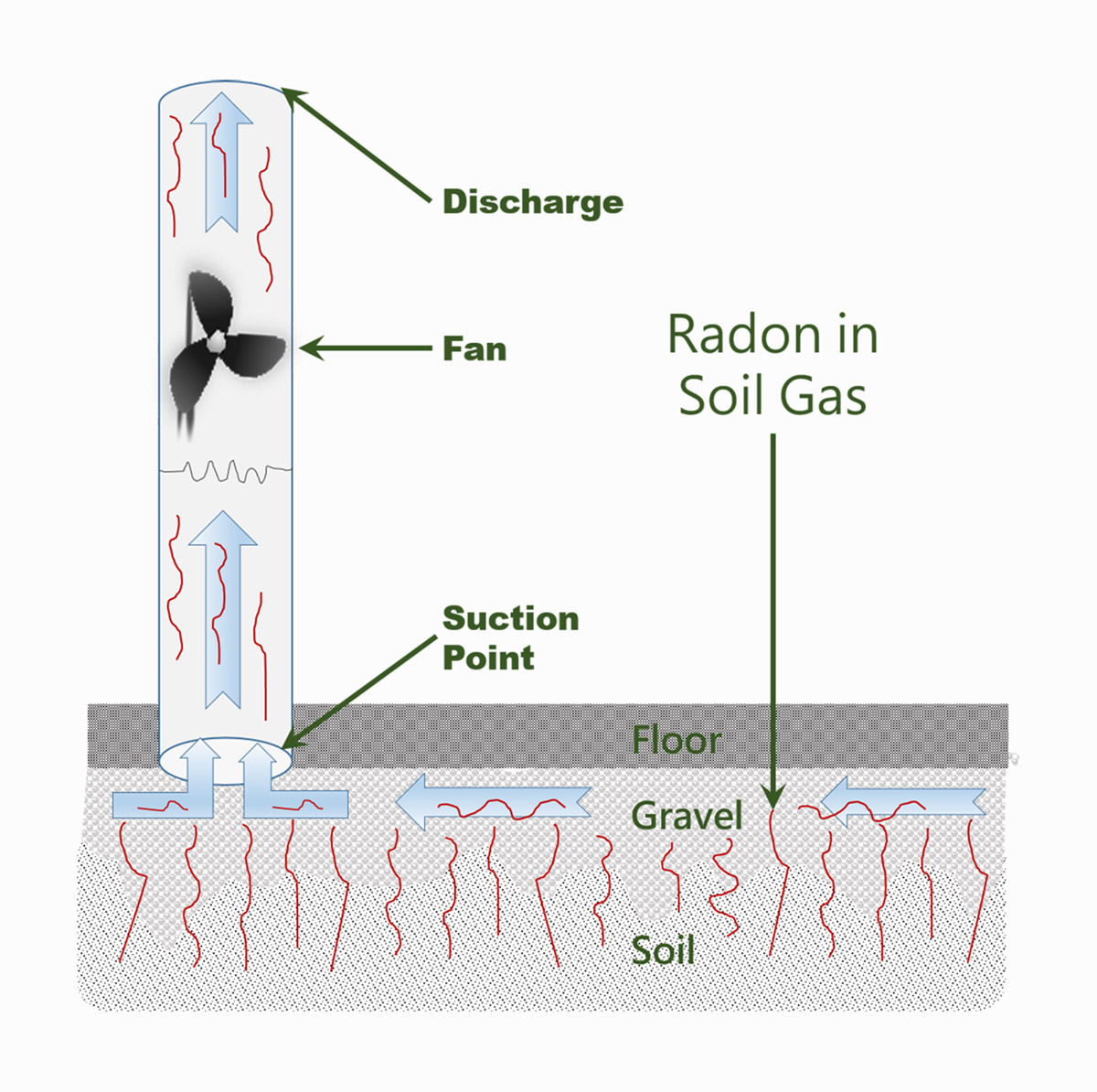
You can take steps to reduce and control the amount of radon in your home, school or workplace. Testing is the only way to determine radon levels. A radon measurement certified professional can test for radon in any application or you can purchase testing DIY kits. If radon levels are high, contact a certified radon mitigation professional to fix your home, school or workplace. EPA guidance suggests mitigating if levels are at or above 148 Becquerels/meter3 (4 picocuries/liter). Usually, radon problems are fixed using an underground ventilation system or by increasing the rate of air changes in the building.